What is Blockchain for Beginners?
Imagine a digital ledger – like a Google Doc or spreadsheet – that’s shared with everyone in a network. Now, imagine that this spreadsheet automatically updates whenever someone makes a change, and that everyone can see these changes in real-time. That’s the basic idea behind blockchain.
But here’s what makes blockchain special: once information is added to this ledger, it can’t be changed or deleted without everyone in the network agreeing to it. It’s like a tamper-proof diary that everyone keeps an identical copy of.
In technical terms, blockchain is a distributed, decentralized public ledger where transactions are recorded in “blocks” that are linked together. Each block contains a batch of transactions, and every time a new transaction occurs, a record of it is added to every participant’s ledger.
The Community-Controlled Spreadsheet
Let’s use a simple metaphor: Imagine you and your friends maintain a shared notebook where you record who owes money to whom. Instead of trusting one person to keep the notebook, everyone gets an identical copy. Whenever someone makes a payment, they announce it to the group, and everyone updates their copy of the notebook.
If someone tries to cheat by changing an entry in their notebook, it won’t match everyone else’s copies, and the group will know something’s wrong. This is essentially how blockchain works – it’s a system built on group verification rather than trusting a single authority.
How Does Blockchain Work?
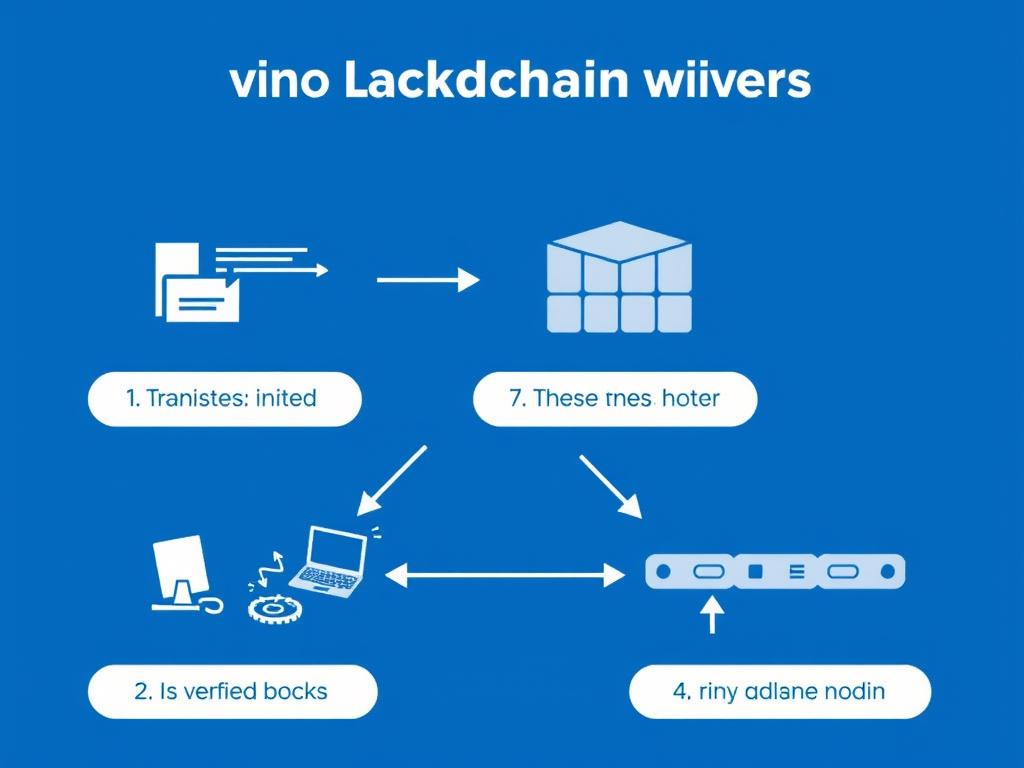
Let’s break down how blockchain works into simple steps:
- Someone requests a transaction – This could be a cryptocurrency payment, a record of a contract, or any other valuable information.
- The transaction is broadcast to a network of computers – These computers (called “nodes”) spread across the globe validate the transaction using known algorithms.
- The verified transaction is combined with others to create a “block” – Think of this as a page in our digital ledger.
- This block is added to the existing “chain” of blocks – Creating a permanent, unalterable record.
- The transaction is complete – And the updated ledger is distributed to all participants in the network.
What Makes Blockchain Secure?
The security of blockchain comes from its structure and the way it stores data. Each block contains:
- The actual transaction data
- A timestamp showing exactly when the block was added
- A unique code called a “hash” that identifies the block
- The hash of the previous block in the chain
This last part is crucial – each block references the one before it, creating a chain where tampering with any block would require changing all subsequent blocks. Since the blockchain is distributed across many computers, a hacker would need to control the majority of computers in the network simultaneously to successfully alter any information – a nearly impossible task.
See Blockchain in Action
Ready to see how transactions flow through a blockchain? Try our interactive demo to visualize the process step-by-step.
Blockchain vs. Cryptocurrency: Understanding the Connection

Many people confuse blockchain with cryptocurrency, but they’re not the same thing. Think of blockchain as the technology platform, and cryptocurrency as just one application built on that platform.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is the underlying technology – a method of storing and tracking information. It can be used for many purposes beyond digital currencies, including:
- Supply chain tracking
- Digital identity verification
- Smart contracts (self-executing contracts)
- Voting systems
- Healthcare record management
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency is digital money that uses blockchain to record and secure transactions. Popular examples include:
- Bitcoin – The first and most well-known cryptocurrency
- Ethereum – Known for its smart contract capabilities
- Litecoin – Designed for faster transaction processing
- Ripple – Focused on international payment transfers
- Cardano – Emphasizes sustainability and scalability
The key takeaway: All cryptocurrencies use blockchain technology, but blockchain has many uses beyond cryptocurrency. It’s like saying all sports cars use engines, but engines are used in many things besides sports cars.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
Decentralization
Unlike traditional systems where a central authority (like a bank) controls the data, blockchain distributes information across a network of computers. No single entity has control, which means there’s no single point of failure or vulnerability.
Transparency
Everyone in the network can see the same information. While personal details remain private through encryption, the transaction data itself is visible to all participants, creating unprecedented transparency.
Immutability
Once data is recorded in a blockchain, it’s extremely difficult to change or delete. This creates a permanent, unalterable history that can be trusted by all parties without needing a middleman to verify information.
Security Through Cryptography
Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data. Each participant has a private key (like a complex password) and a public key (like an account number). The private key creates a digital signature that verifies transactions without revealing the key itself.
Consensus Mechanisms
For a transaction to be added to the blockchain, a majority of the network must agree it’s valid. Different blockchains use different methods to reach this agreement, including:
- Proof of Work – Computers solve complex puzzles to validate transactions (used by Bitcoin)
- Proof of Stake – Validators are chosen based on how many coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral
- Delegated Proof of Stake – Token holders vote for representatives who validate transactions
Benefits of Blockchain Technology

Enhanced Security
The decentralized nature of blockchain makes it extremely difficult to hack or alter data. Each transaction is encrypted and linked to previous transactions, creating a secure chain that’s nearly impossible to tamper with.
Greater Transparency
All network participants have access to the same information, creating a single source of truth. This transparency builds trust between parties who might not otherwise have reason to trust each other.
Increased Efficiency
By eliminating intermediaries and automating verification processes, blockchain can significantly reduce transaction times and costs. What might take days through traditional systems can happen in minutes.
Improved Traceability
Every transaction is recorded chronologically and permanently. This creates an audit trail that can track assets or information from origin to destination, which is particularly valuable in supply chains.
Reduced Costs
By removing the need for third-party verification, blockchain can eliminate many administrative costs and fees associated with transactions, contracts, and record-keeping.
Smart Contracts
These are self-executing contracts where the terms are written directly into code. When predetermined conditions are met, the contract automatically executes, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
Stay Updated on Blockchain Innovations
The world of blockchain is evolving rapidly. Subscribe to our newsletter to receive the latest updates, tutorials, and insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain

Blockchain technology extends far beyond cryptocurrency. Here are some of the most promising applications already being implemented:
Supply Chain Management
Companies like Walmart and Maersk use blockchain to track products from origin to store shelf. This allows for quick identification of contaminated food sources or counterfeit products, and provides consumers with verified information about product origins.
Healthcare Records
Blockchain can securely store patient records while giving patients control over who accesses their information. This improves data security, reduces administrative errors, and allows for seamless sharing between authorized healthcare providers.
Voting Systems
Blockchain-based voting platforms can create tamper-proof election records, potentially reducing fraud and increasing participation through secure online voting options.
Digital Identity
Blockchain can provide secure, self-sovereign identity solutions that give individuals control over their personal information while reducing identity theft and fraud.
Financial Services
Beyond cryptocurrency, banks and financial institutions are exploring blockchain for faster, cheaper cross-border payments, simplified trade finance, and automated compliance processes.
Types of Blockchain Networks
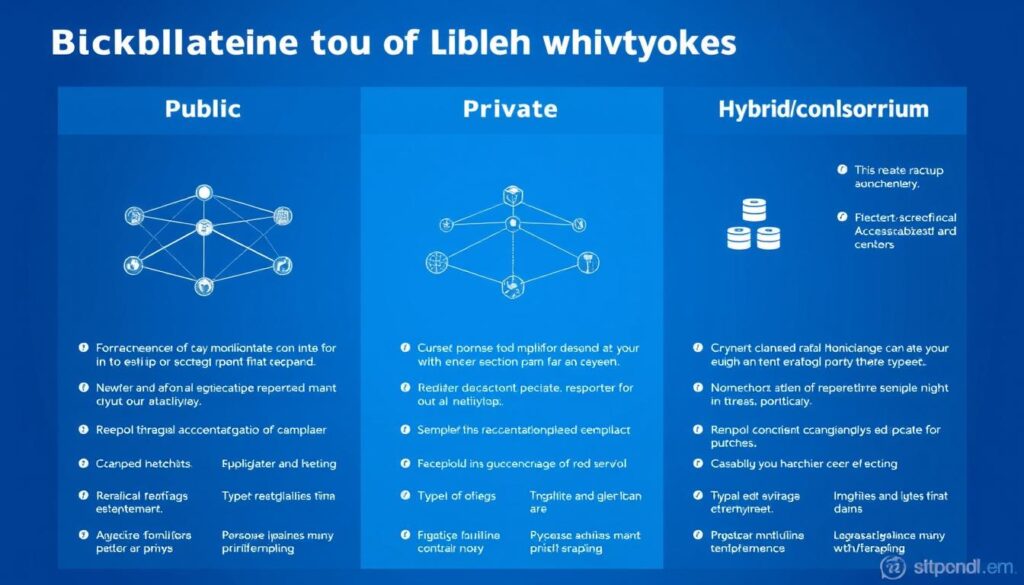
Not all blockchains are created equal. There are several different types, each with unique characteristics suited to different purposes:
| Type | Access | Examples | Best For | Limitations |
| Public Blockchain | Open to anyone | Bitcoin, Ethereum | Cryptocurrency, applications requiring maximum transparency | Slower transaction speeds, higher energy consumption |
| Private Blockchain | Restricted to authorized participants | Hyperledger Fabric, Corda | Business applications, situations requiring data privacy | Less decentralized, requires trusted authority |
| Consortium Blockchain | Controlled by a group of organizations | Energy Web Chain, Marco Polo Network | Cross-industry collaboration, regulated industries | More complex governance, potential for power imbalances |
| Hybrid Blockchain | Combination of public and private features | Dragonchain, XDC Network | Organizations needing both privacy and transparency | More complex architecture, newer technology |
The type of blockchain that’s best for a particular use case depends on factors like required transaction speed, privacy needs, and who needs access to the data.
Understanding Smart Contracts
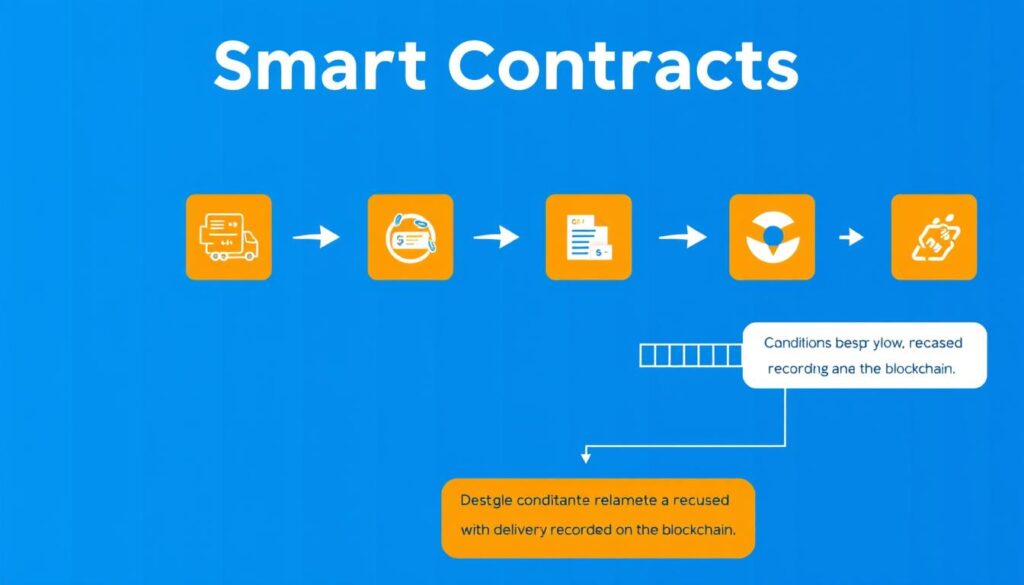
Smart contracts are perhaps one of the most revolutionary aspects of blockchain technology. Think of them as self-executing digital contracts where the terms are written directly into code.
How Smart Contracts Work
A smart contract functions like a digital vending machine. Just as a vending machine automatically dispenses a product when you insert money and make a selection, a smart contract automatically executes actions when predetermined conditions are met.
For example, a smart contract might say: “When Person A transfers the agreed amount to Person B, automatically transfer ownership of the digital asset to Person A.” Once the payment is verified on the blockchain, the ownership transfer happens automatically – no lawyers, notaries, or other intermediaries required.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
- Automation – Executes automatically when conditions are met
- Accuracy – Digitally encoded terms eliminate ambiguity
- Speed – Processes happen in minutes rather than days or weeks
- Trust – No need to trust the other party; the code enforces the agreement
- Cost Reduction – Eliminates intermediaries and their associated fees
Real-World Applications
Smart contracts are already being used for:
- Insurance claims that pay out automatically when certain conditions are verified
- Supply chain management to automatically release payment when goods are received
- Real estate transactions to automate payments and property transfers
- Royalty payments that automatically distribute funds when digital content is used
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain

While blockchain offers many benefits, it’s not without challenges. Understanding these limitations is important for anyone exploring the technology:
Strengths
- Highly secure and tamper-resistant
- Transparent and verifiable
- Eliminates need for intermediaries
- Reduces fraud and errors
- Creates permanent, time-stamped records
Challenges
- Scalability issues with some networks
- High energy consumption (especially Proof of Work)
- Complex technology with steep learning curve
- Regulatory uncertainty in many jurisdictions
- Integration difficulties with legacy systems
The Scalability Trilemma
Blockchain developers often talk about the “scalability trilemma” – the challenge of achieving scalability, security, and decentralization simultaneously. Most current blockchain solutions excel at two of these aspects but compromise on the third.
For example, Bitcoin prioritizes security and decentralization but has limited transaction throughput. Other blockchains might increase speed by reducing the number of validators, which impacts decentralization.
Evolving Solutions
The good news is that the blockchain community is actively working on solutions to these challenges, including:
- Layer 2 solutions – Additional frameworks built on top of existing blockchains to improve scalability
- Proof of Stake – More energy-efficient consensus mechanisms
- Sharding – Breaking the network into smaller pieces to process transactions in parallel
- Cross-chain technology – Allowing different blockchains to communicate and work together
Getting Started with Blockchain

Ready to dive deeper into blockchain? Here’s a simple checklist to get you started:
- Educate yourself – Continue learning through books, online courses, and reputable websites focused on blockchain technology.
- Set up a digital wallet – Try a user-friendly wallet like Coinbase Wallet or MetaMask to experience blockchain firsthand.
- Make a small cryptocurrency purchase – Buy a small amount of a major cryptocurrency to understand the transaction process.
- Explore blockchain explorers – Use tools like Etherscan or Blockchain.com Explorer to view real transactions on public blockchains.
- Join communities – Participate in forums like Reddit’s r/blockchain or Discord channels to connect with others learning about blockchain.
Recommended Tools for Beginners
Digital Wallets
- Coinbase Wallet
- MetaMask
- Trust Wallet
Blockchain Explorers
- Etherscan
- Blockchain.com Explorer
- BTC.com
Learning Platforms
- Coursera
- Udemy
- Codecademy

Frequently Asked Questions
Is blockchain only for cryptocurrencies?
No, cryptocurrency is just one application of blockchain technology. Blockchain can be used for supply chain management, digital identity verification, voting systems, healthcare records, and many other applications that benefit from secure, transparent record-keeping.
Is blockchain completely secure?
While blockchain is highly secure by design, no technology is 100% immune to all threats. The main blockchain structure is extremely difficult to hack, but surrounding systems (like exchanges or wallets) may have vulnerabilities. That said, blockchain is generally considered one of the most secure ways to store and transfer digital information.
How much technical knowledge do I need to use blockchain?
For basic use as a consumer (like making cryptocurrency transactions), you don’t need technical knowledge. User-friendly apps and interfaces handle the complexity. However, to develop blockchain applications or work professionally in the field, you would need to learn specific programming languages and blockchain concepts.
Does blockchain use a lot of energy?
Some blockchain networks, particularly those using Proof of Work consensus mechanisms like Bitcoin, do consume significant energy. However, newer blockchain technologies using Proof of Stake and other alternative consensus mechanisms are much more energy-efficient. The industry is actively working to reduce its environmental impact.
Can blockchain records be deleted or changed?
By design, blockchain creates permanent, immutable records. Once data is added to the blockchain and confirmed by the network, it becomes extremely difficult to alter or delete. This immutability is one of blockchain’s key features, ensuring that records remain trustworthy and tamper-proof.
Recommended Resources for Further Learning

Ready to continue your blockchain journey? Here are some excellent resources to deepen your understanding:
Books
- “Blockchain Basics” by Daniel Drescher
- “Blockchain Revolution” by Don Tapscott
- “The Basics of Bitcoins and Blockchains” by Antony Lewis
Online Courses
- “Blockchain Fundamentals” on Coursera
- “Blockchain A-Z” on Udemy
- “Blockchain Essentials” on edX
Websites & Communities
- Coindesk.com
- Reddit’s r/blockchain
- GitHub blockchain projects
Download Your Free Blockchain Basics Guide
Want to take this knowledge with you? Get our comprehensive Blockchain Basics PDF guide with additional examples, glossary of terms, and a roadmap for continued learning.
Conclusion: The Future of Blockchain

Blockchain technology is still in its early stages, comparable to where the internet was in the mid-1990s. Just as few people could predict how the internet would transform our lives, we’re only beginning to see the potential impact of blockchain.
As the technology matures, we can expect more user-friendly applications, greater scalability, and integration with other emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things. Regulatory frameworks will likely evolve to provide clearer guidelines while preserving innovation.
Whether you’re interested in blockchain as an investment opportunity, a career path, or simply as an informed citizen of our increasingly digital world, understanding the fundamentals puts you ahead of the curve. The decentralized, transparent nature of blockchain has the potential to reshape how we transfer value, verify identity, and establish trust in our digital interactions.
Remember, you don’t need to understand every technical detail to appreciate blockchain’s significance. Just as most of us use the internet without knowing how TCP/IP protocols work, you can benefit from blockchain applications without mastering all its complexities.
Keep learning, stay curious, and watch as this transformative technology continues to evolve and reshape our digital landscape.
Ready to Take the Next Step?
Join our community of blockchain enthusiasts to continue learning, share insights, and stay updated on the latest developments in this exciting field.
FAQ
1. What is blockchain in simple terms?
Blockchain is like a shared digital notebook where everyone can see and verify each entry. Once something is written, it can’t be changed without group approval. It’s secure, transparent, and decentralized.
2. Is blockchain the same as Bitcoin or cryptocurrency?
No. Blockchain is the technology, while cryptocurrency like Bitcoin is one of its uses. Blockchain can also be used in supply chains, healthcare, voting systems, and more.
3. How does a transaction get added to the blockchain?
A transaction is requested, verified by a network of computers, grouped into a block, and added to the chain. Once confirmed, it becomes a permanent record.
4. Why is blockchain considered secure?
Blockchain uses cryptography, timestamps, and a unique hash system. Every block is linked to the one before it, making tampering nearly impossible across the entire network.
5. Can anyone use blockchain without technical knowledge?
Yes. You can use apps like digital wallets and exchanges to make crypto transactions without knowing the technical details. However, building on blockchain does require coding skills.
6. What is a smart contract?
A smart contract is a self-running digital agreement coded to automatically execute actions when conditions are met — like transferring payment or ownership.
7. Does blockchain use a lot of energy?
Some blockchains like Bitcoin use energy-heavy processes (Proof of Work). Others use more eco-friendly methods like Proof of Stake, which consume much less energy.
8. Is it possible to delete or change information on the blockchain?
No. Once data is verified and added to the blockchain, it becomes immutable, meaning it can’t be deleted or changed without the network’s consensus.
9. What are some real-world uses of blockchain besides cryptocurrency?
Blockchain is used in:
Supply chains (e.g., tracking products)
Healthcare (secure patient records)
Voting systems (tamper-proof elections)
Digital identity (fraud prevention)
Finance (faster cross-border payments)
10. What’s the future of blockchain technology?
Blockchain is still evolving. Future trends include more scalable networks, eco-friendly consensus methods, and integration with AI and IoT. It’s expected to transform industries the way the internet once did.


